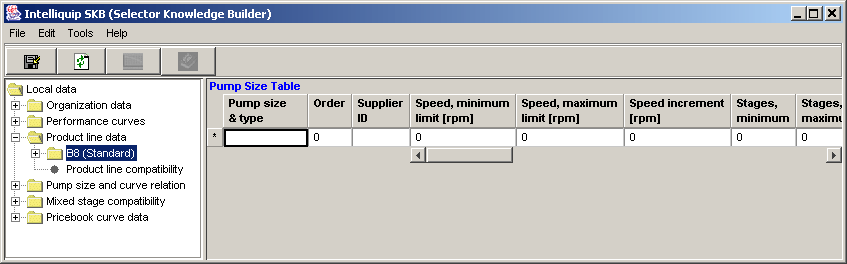
The Pump Size Table houses the individual pump information
for the product lines. The table is designed to capture data specific
for each pump size thus allowing each pump's behavior to be controlled.
The table also provides functionality to control what pumps are available
in the Selector, this allows the database to be populated regardless if
pumps are in production or still in development. See below to learn how
to populate the table and about the information it houses.
This image shows
the B8 (Standard) product line is selected.
Pump size and type Enter a unique pump size and type for each pump in the product line.
This information will be visible in the Selector to identify the different
pumps.
Order Enter a numerical value representing the order placement for which the
pump size are to be displayed. Pumps are displayed in ascending order.
(1,2,3,4, etc.).
Supplier ID Enter a specific ID for each pump size. ID's must be unique for every
pump size in an organization. Pump ID's will be displayed in the Selector's
pump size list table.
Speed, minimum limit [rpm] Enter the minimum speed range for the pump.
Remember a pump can be represented by more than one curve, the speed range
must take this into account when applicable. Below show a typical example
of a pump using three separate curves.
Curve1: 1800 to 3600RPM (2 pole).
Curve2: 1200 to 1800RPM (4 pole).
Curve3: 900 to 1200RPM (6 pole).
Pump's, speed range: 901 to 3600RPM.
Rule: The rated speed > curve minimum limit and the rated speed <=
curve max limit.
Speed, maximum limit [rpm] Enter the maximum speed range for the pump. Remember a pump can be represented
by more than one curve, the speed range must take this into account when
applicable. Below show a typical example of a pump using three separate
curves.
Curve1: 1800 to 3600RPM (2 pole).
Curve2: 1200 to 1800RPM (4 pole).
Curve3: 900 to 1200RPM (6 pole).
Pump's, speed range: 901 to 3600RPM.
Rule: The rated speed > curve minimum limit and the rated speed <=
curve max limit.
Speed increment [rpm] Enter the increment be used to round any speed which is calculated
as a result of the user's Hz or the Selector performing a speed reduction
calculation.
Stages, minimum Enter the minimum number of stages supported by the pump. The minimum
must be greater than zero.
Stages, maximum Enter the maximum number of stages supported by the pump.
Allowable stages If applicable, enter the allowable stages that a pump can be selected
between the minimum and maximum stage limits. The Selector will evaluate
to the stages specified en lieu of any stage between the minimum and maximum
values.
Example: A multistage pump has a stage range from 1-10, however it's only
manufactured in 1,2,4,6,8,& 10 stages. Therefore to limit the stages
the allowable stage field is populated as follows: 1:2:4:6:8:10
Shaft power limit [kW/1000rpm] Enter a value that represents the strongest shaft material that can
be supplied with the pump.
Solids diameter limit [mm] Enter the maximum solids diameter that can be handled by the pump.
Cutwater diameter
[mm] The cutwater diameter ratio (shown in search results
and the performance datasheet) = Rated diameter / cutwater
diameter.
Variable speed, minimum limit [rpm] This field is only applicable when using the "Multi-Speed Curve"
page in the Selector. If applicable, populate the minimum speed limit
that is acceptable for the pump size when using the multi-speed page.
If set to zero, the curve minimum speed will be used. This limit can also
be set at the curve level. If both are in use (not zero), the curve boundary
level will take precedence.
Reject margin, minimum speed [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for minimum speed that
a "near miss" will result. Any selection within the margin will
be considered a "near miss", any selection
below the margin will be considered a full reject and discarded. For example:
a pump's minimum speed is 500 rpm with a designated reject margin for
minimum speed of 10%, as a result for any speed >= 450 rpm and <500
rpm the Selector will return a "near miss" and for any speed
< 450 rpm a full reject will occur.
Note: Regardless of the margin defined, if the curve's minimum speed is
exceeded a full reject will occur.
Reject margin, maximum speed [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for maximum speed that
a "near miss" will result. Any selection within the margin will
be considered a "near miss", any selection
above the margin will be considered a full reject and discarded. For example:
a pump's maximum speed is 1800 rpm with a designated reject margin for
minimum speed of 10%, as a result for any speed >1800 rpm and <
= 1980 rpm the Selector will return a "near miss" and for any
speed > 1980 rpm a full reject will occur.
Note: Regardless of the margin, if the curve's maximum speed is exceeded
the pump will be considered a full reject and discarded.
Reject margin, maximum flow [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for maximum flow that
a "near miss" will result. The maximum flow value is determined
by the end of curve point. Any selection within the margin will be considered
a "near miss", any selection outside
the margin will be considered a full reject and discarded.
Reject margin, minimum head [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin
for minimum head that a "near miss" will result. Any selection
within the margin will be considered a "near
miss", any selection outside the margin will be considered a full
reject and discarded. Click the below links to see examples on how margins
are applied.
-
-
-
-
Reject margin, maximum head [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for maximum head that
a "near miss" will result. Any selection within the margin will
be considered a "near miss", any selection
outside the margin will be considered a full reject and discarded. Click
the below links to see examples on how margins are applied.
-
-
-
-
Reject margin, MCSF [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for minimum continuos
staple flow (MCSF) that a "Near Miss" will result. Any selections
outside the margin will be discarded. MCSF values are defined at the curve
level in the General
Curve Table.
Reject margin, shaft power [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for shaft power that
a "Near Miss" will result. Any selections outside the margin
will be discarded. Shaft power limits are defined in the Shaft power limit
[kW/1000rpm] field.
Reject margin, NPSH [%] Enter a percent value for the allowable margin for NSPH that a "near
miss" will result. Any selection within the margin will be considered
a "near miss", any selection below the
margin will be considered a full reject and discarded. NPSH values are
determined at the curve level in NPSH
point data tables.
Viscous CE limit for near miss If necessary, enter a value for the allowable limit for the viscous
coefficient for efficiency that a "Near Miss" will result. Any
selections outside the margin will be considered a full reject.
Viscous CE limit for full reject If necessary, enter a value for the allowable limit for the viscous
coefficient for efficiency that a "Full reject" will result.
Any selections outside the margin will be discarded.
Compatibility
rule
Status This selection box contains selections to activate, disable, or conceal
a pump in the Selector.
Select ”Active” to enable a pump. An "active" pump will be available
in the Selector after the next successful deployment sequence.
Select ”Redundant” to disable a pump. A "redundant" pump will
not be available in the Selector after a deployment sequence or be removed
from the Selector if its status was "active" in a prior deployment.
This feature allows the database to be populated with pumps in production
or under development eliminating the need for two separate databases.
Select "Conceal" to hide a pump in the search results and size
list pages in the Selector. It will be displayed in the Selector's performance
datasheet mixed stage performance section when using mixed
stage compatibility table.